Advanced Data Visualization Techniques
Sarah Cassie Burnett
September 16, 2025
Announcements
- Online quiz posted at the end of class, due tomorrow.
- Coding Assignment 1 is due by 11:59 pm tonight.
- Submit the assignment on Gradescope.
- Minor final project assignment due Thursday.

Last class
- Column charts (bar charts)
- Use to compare values across categories
- Histograms
- Use to show distribution of a single variable
- Line charts
- Use to show trends over time
- Can use column charts but not as effective
- Scatter plots
- Use to show relationships between two variables
- X-axis is usually explanatory variable, Y-axis is outcome variable
Other Plots and Geometries
Box Plot
geom_boxplot()Violin Plot
geom_violin()Density Plot
geom_density()Bar Plot (Categorical)
geom_bar()Heatmap
geom_tile()
Area Plot
geom_area()Dot Plot
geom_dotplot()Pie Chart
(usually a bar plot withcoord_polar())Ridgeline Plot
ggridges::geom_density_ridges()Map Plot (Choropleth)
geom_polygon()
The Grammar of Graphics
- Data viz has a language with its own grammar
- Basic components include:
- Data we are trying to visualize
- Aesthetics (dimensions)
- Geom (e.g. bar, line, scatter plot)
- Color scales
- Themes
- Annotations
Resources
- Have a look at the documentation for ggplot2
- Familiarize yourself with the
ggplot2cheatsheet
Fill vs. Color
- Use color (e.g.
color =orscale_color_*) to modify the color of points, lines, or text. - Commonly applied to:
- Scatter plots
- Line charts
- Text elements
Fill vs. Color
- Use fill (e.g.
fill =orscale_fill_*) to modify the fill color of shapes like bars, boxes, or polygons. - Commonly applied to:
- Bar charts
- Box plots
- Histograms
Load & Clean Film Data
Histogram: Award-Winning Movie Lengths (by Genre)
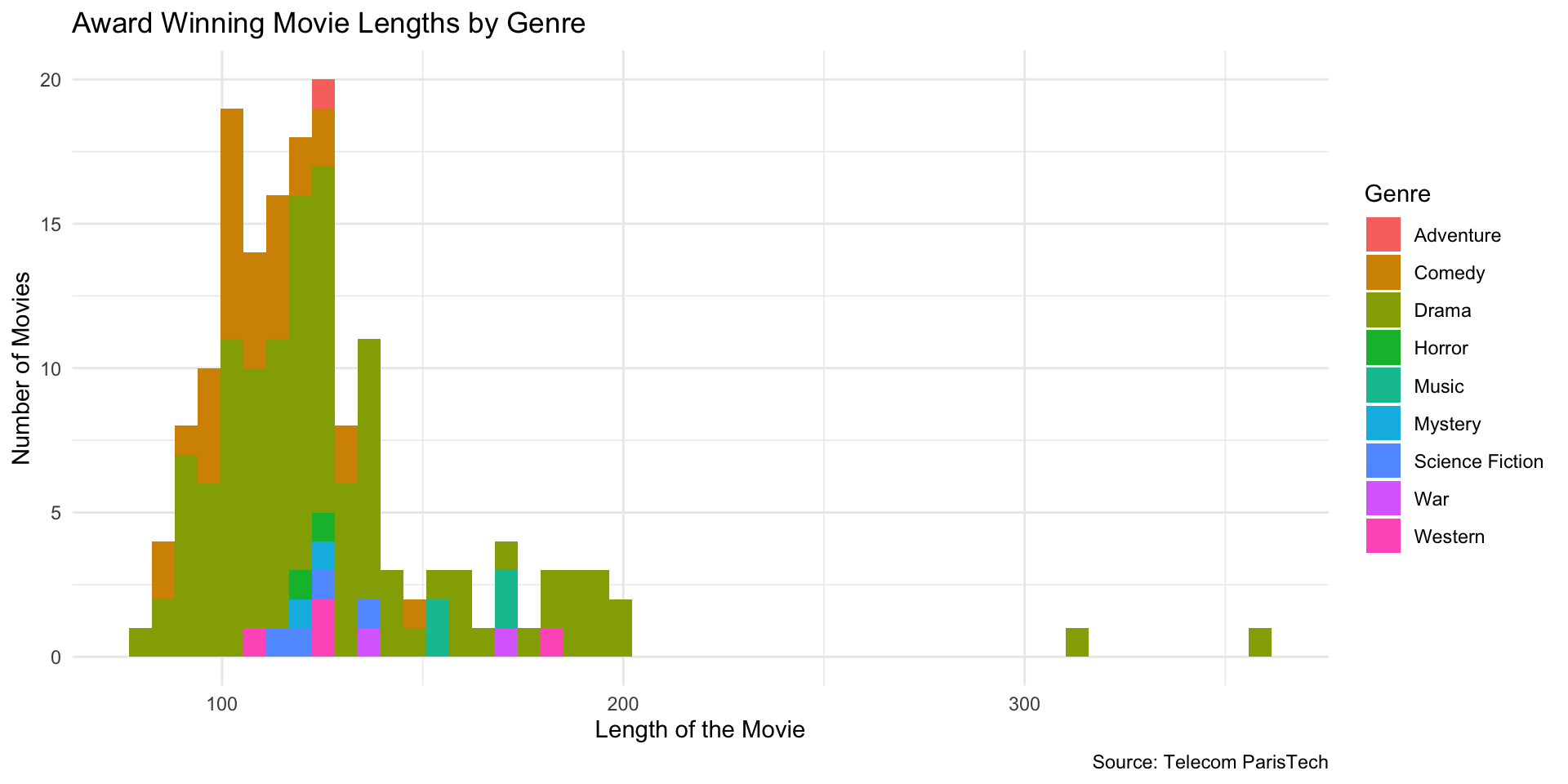
Histogram: Award-Winning Movie Lengths
Overlay Two Groups
(Drama vs Not Drama)
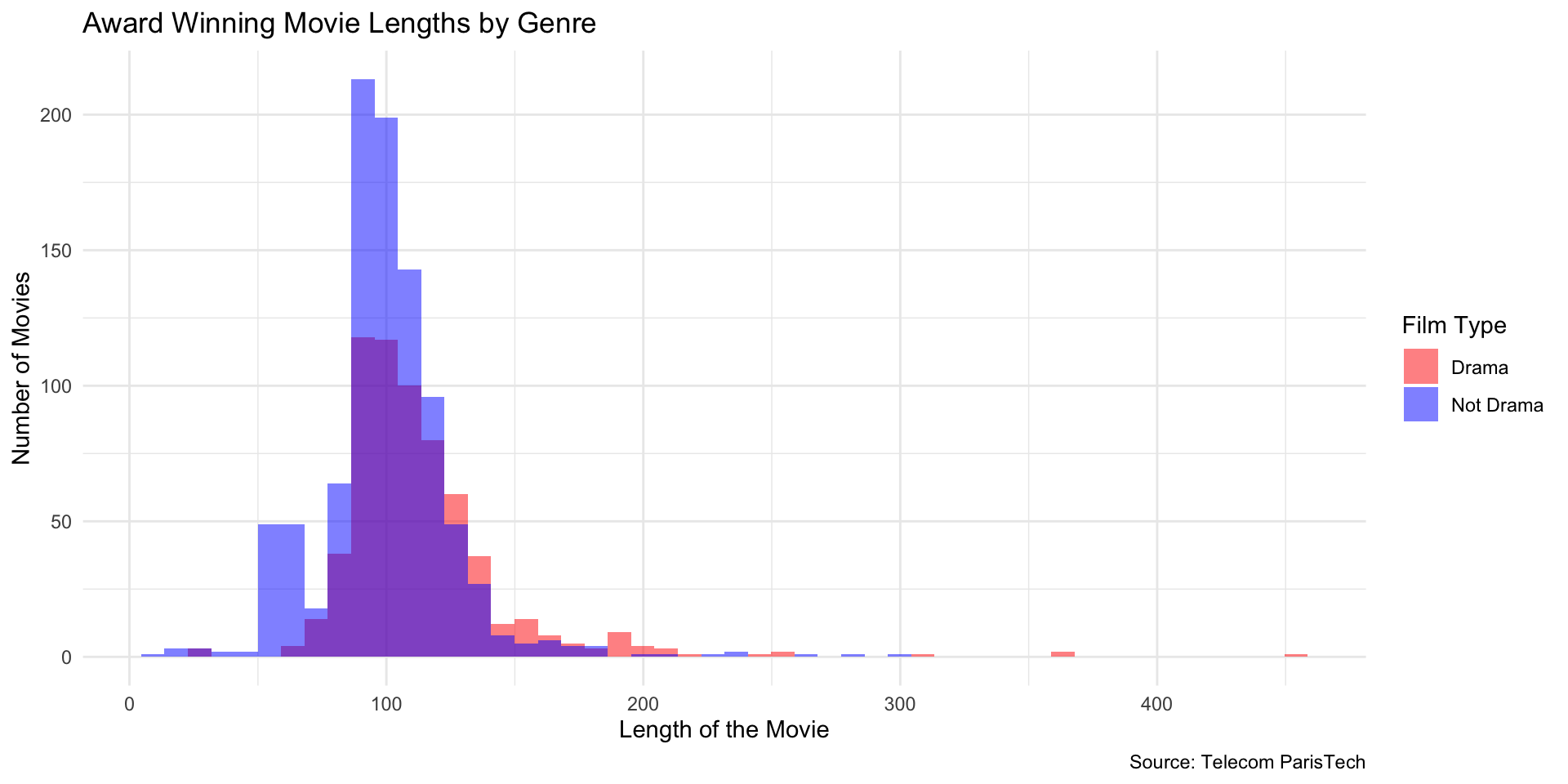
Overlay Two Groups (Drama vs Not Drama)
drama_films <- films |> filter(Genre == "Drama")
not_drama_films <- films |> filter(Genre != "Drama")
ggplot() +
geom_histogram(data = drama_films, aes(x = Length, fill = "Drama"),
alpha = 0.5, bins = 50) +
geom_histogram(data = not_drama_films, aes(x = Length, fill = "Not Drama"),
alpha = 0.5, bins = 50) +
labs(
x = "Length of the Movie",
y = "Number of Movies",
title = "Award Winning Movie Lengths by Genre",
caption = "Source: Telecom ParisTech",
fill = "Film Type"
) +
theme_minimal()Manually add the scale values.
drama_films <- films |> filter(Genre == "Drama")
not_drama_films <- films |> filter(Genre != "Drama")
ggplot() +
geom_histogram(data = drama_films, aes(x = Length, fill = "Drama"),
alpha = 0.5, bins = 50) +
geom_histogram(data = not_drama_films, aes(x = Length, fill = "Not Drama"),
alpha = 0.5, bins = 50) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Drama" = "red", "Not Drama" = "blue")) +
labs(
x = "Length of the Movie",
y = "Number of Movies",
title = "Award Winning Movie Lengths by Genre",
caption = "Source: Telecom ParisTech",
fill = "Film Type"
) +
theme_minimal()Use mutate to instead create a new column of data with this information
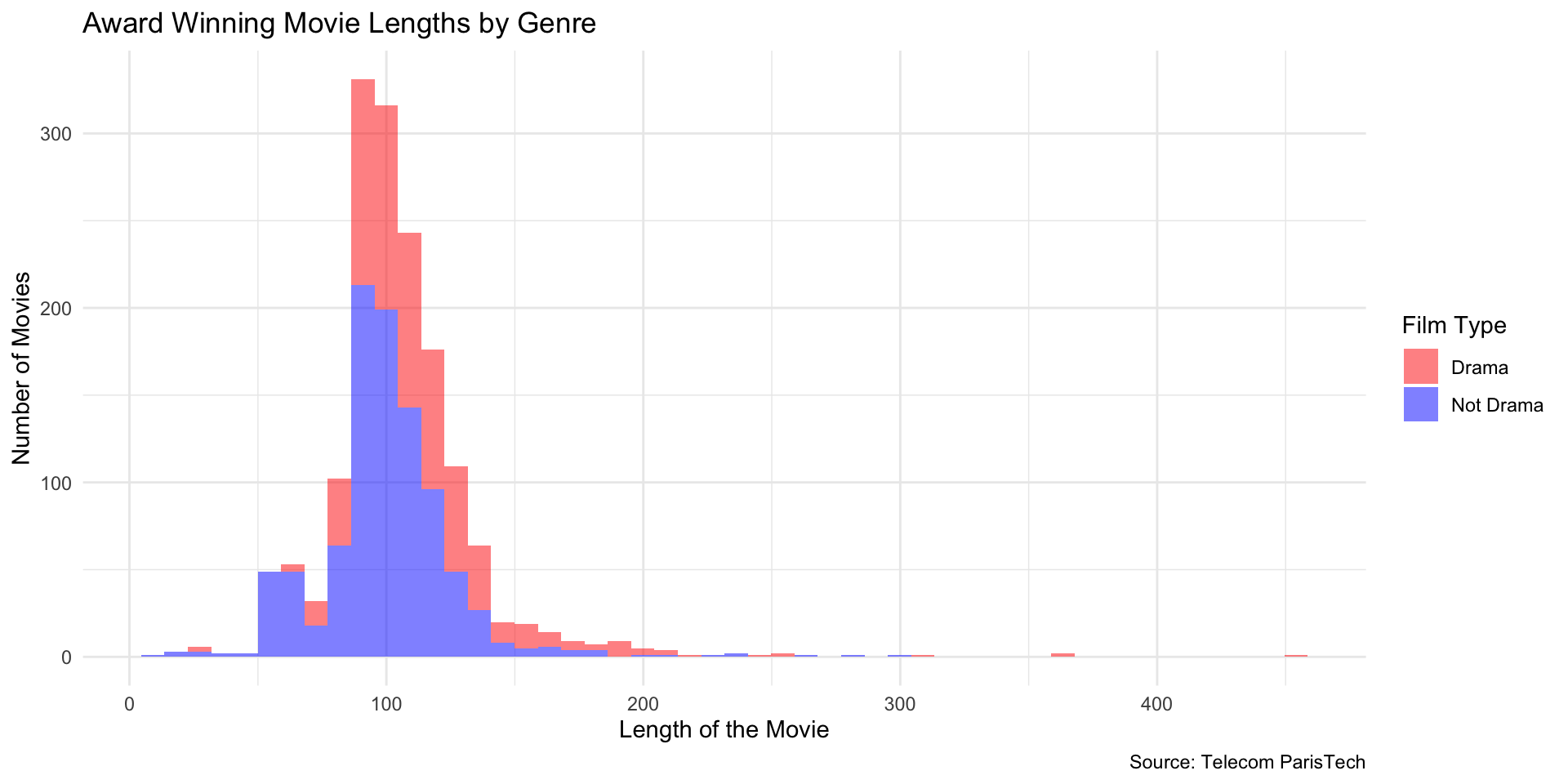
Use mutate to instead create a new column of data with this information
films2 <- films |>
mutate(GenreType = if_else(Genre == "Drama", "Drama", "Not Drama"))
ggplot(films2, aes(x = Length, fill = GenreType)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 50, alpha = 0.5) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Drama" = "red", "Not Drama" = "blue")) +
labs(
x = "Length of the Movie",
y = "Number of Movies",
title = "Award Winning Movie Lengths by Genre",
caption = "Source: Telecom ParisTech",
fill = "Film Type"
) +
theme_minimal()Faceted Histogram (Drama vs Not Drama)
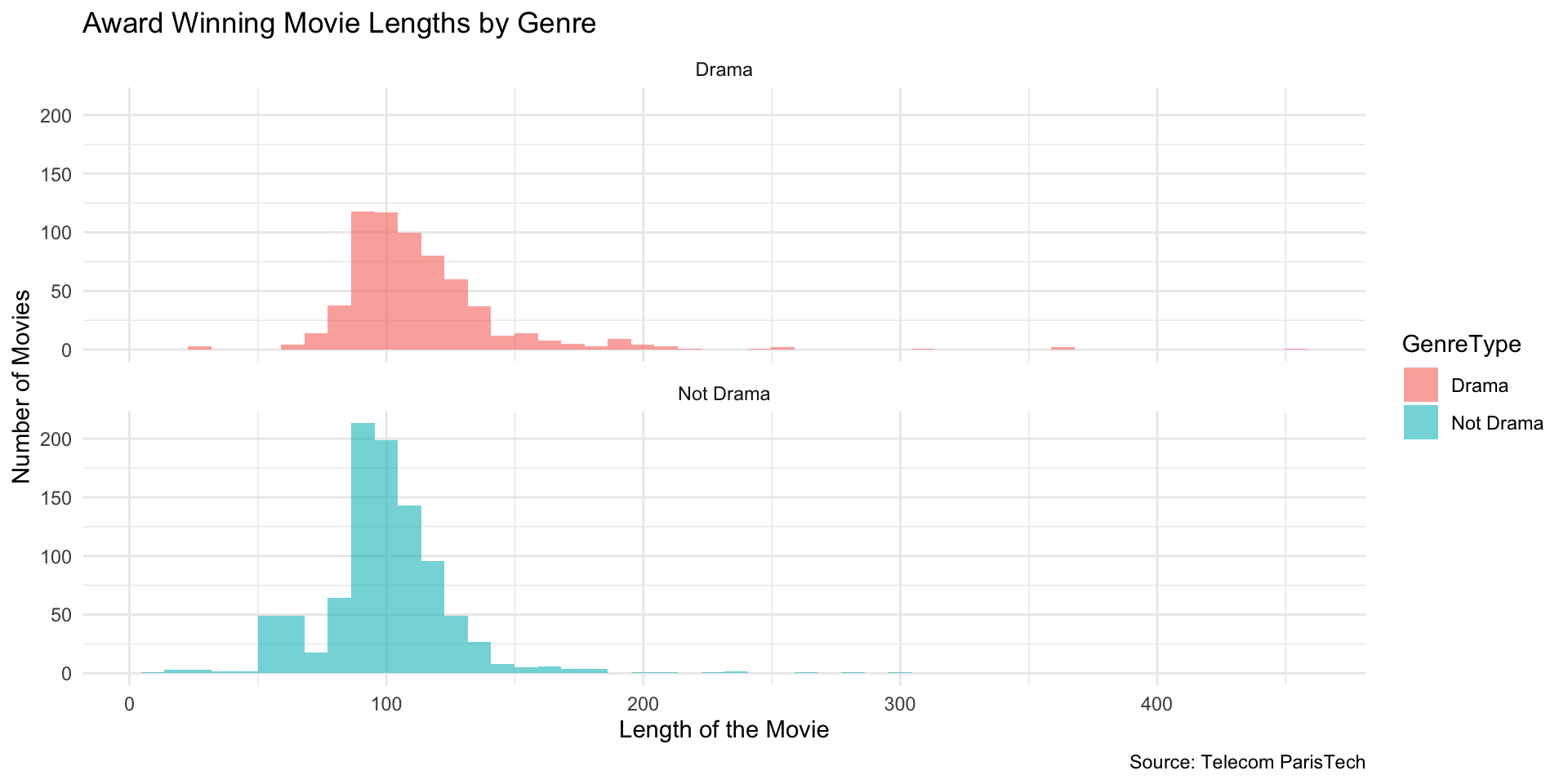
Faceted Histogram (Drama vs Not Drama)
Save Plots (PNG / PDF / RDS)
Diamonds: Range Check
[1] 326[1] 18823[1] 57.73926Over 50x difference
Diamonds: Linear Histogram (Counts)
Diamonds: Log Scale on X (Counts)
Note
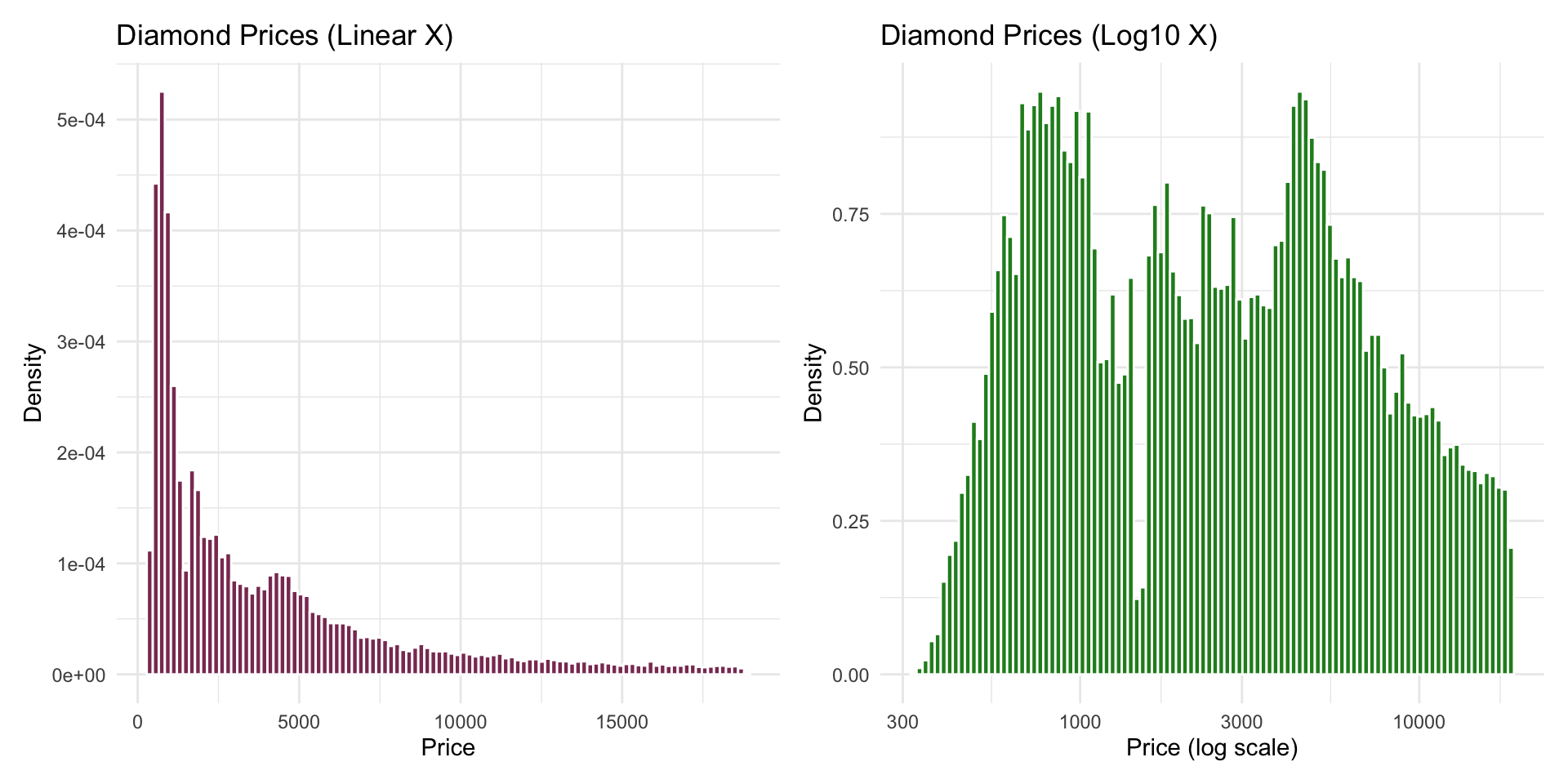
Linear bins vs. Log bins
- Linear: equal dollars per bin (e.g., 0–300, 300–600, 600–900, …)
- Log10: equal factors per bin (e.g., 10^2 – 10^2.1, 10^2.1 – 10^2.2, …) or (about 100 – 126, …, 10000 – 12600)
Density Comparison: Linear vs Log (Side-by-Side)
library(patchwork)
d_linear <- ggplot(diamonds, aes(x = price, y = after_stat(density))) +
geom_histogram(bins = 100, fill = "hotpink4", color = "white") +
labs(
title = "Diamond Prices (Linear X)",
x = "Price",
y = "Density"
) +
theme_minimal()
d_log <- ggplot(diamonds, aes(x = price, y = after_stat(density))) +
geom_histogram(bins = 100, fill = "forestgreen", color = "white") +
scale_x_log10() +
labs(
title = "Diamond Prices (Log10 X)",
x = "Price (log scale)",
y = "Density"
) +
theme_minimal()
d_linear + d_log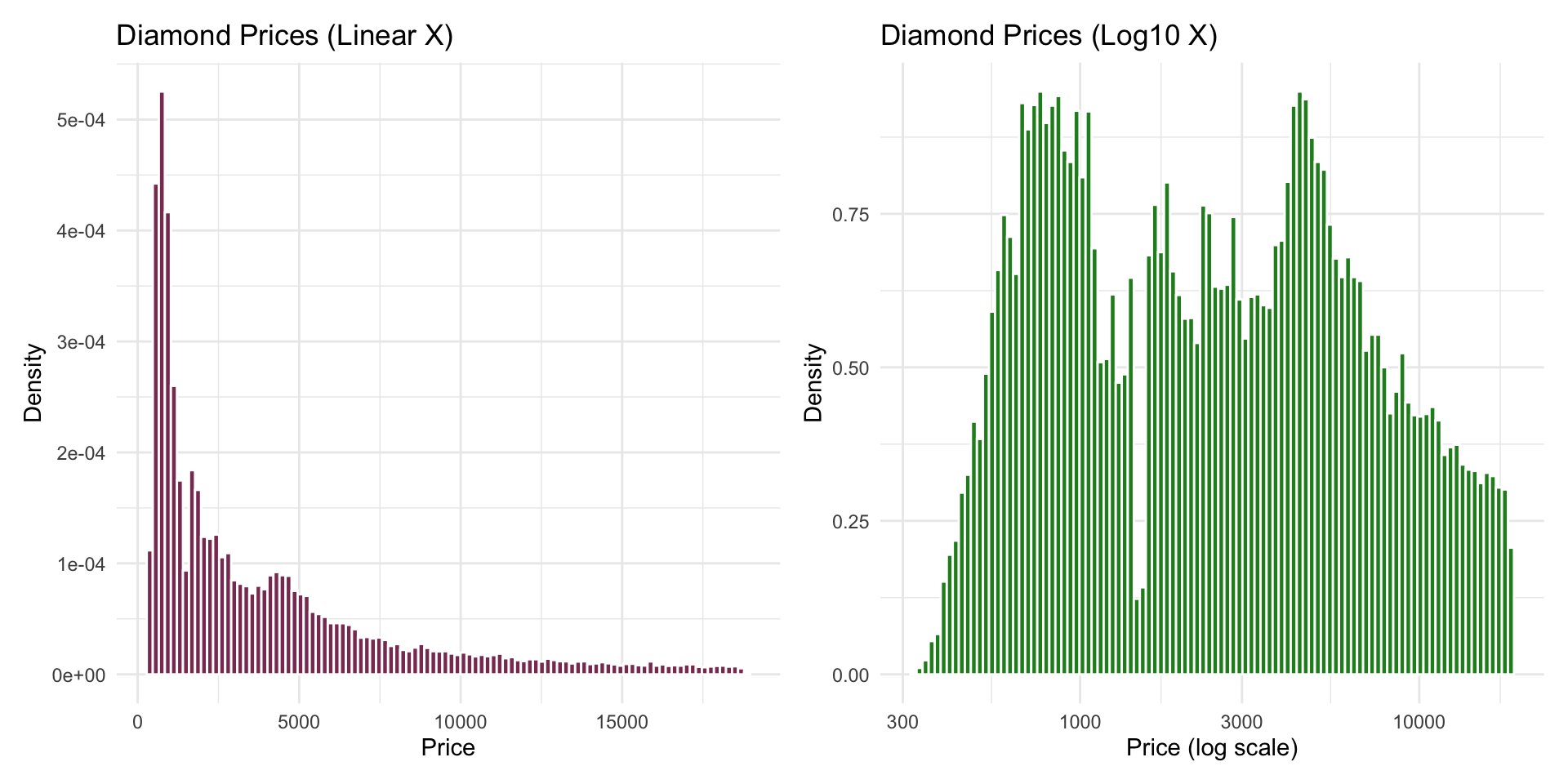
Density Comparison: Linear vs Log (Side-by-Side)
Color Scales: Viridis (Discrete)
Resources
- ggplot2 docs: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org/
- Data viz cheatsheet: https://posit.co/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/data-visualization-1.pdf
Find Your Own Data
- Visit kaggle.com
- Find a dataset you like
- Download it as a CSV
- Read it into R
- Explore with
glimpse()andView()
05:00