Measuring Distributions
Sarah Cassie Burnett
October 16, 2025
Recap: Describing a Distribution
When summarizing a dataset, report all four key features:
- Center — e.g., mean or median
- Spread — e.g., IQR or standard deviation
- Shape — e.g., skewness, modality (unimodal, bimodal)
- Unusual points — e.g., outliers or extreme values
Recap: Describing Distributions
Last time, we focused on two main features of a distribution:
- Center — the typical value (mean or median)
- Spread — how far values vary from that center
Together, these give a complete summary of a dataset’s pattern.
Center: Mean vs. Median
- Mean works well when data is symmetric and not affected by outliers.
- Median is robust — it’s better when the data are skewed or have extreme values.
- For bimodal or multimodal data,
- your data could need to be separated into groups first, or
- your data could be under sampled.
Undersampled vs. Well-sampled
Let’s look at penguin flipper length.
Here’s a histogram across three species:
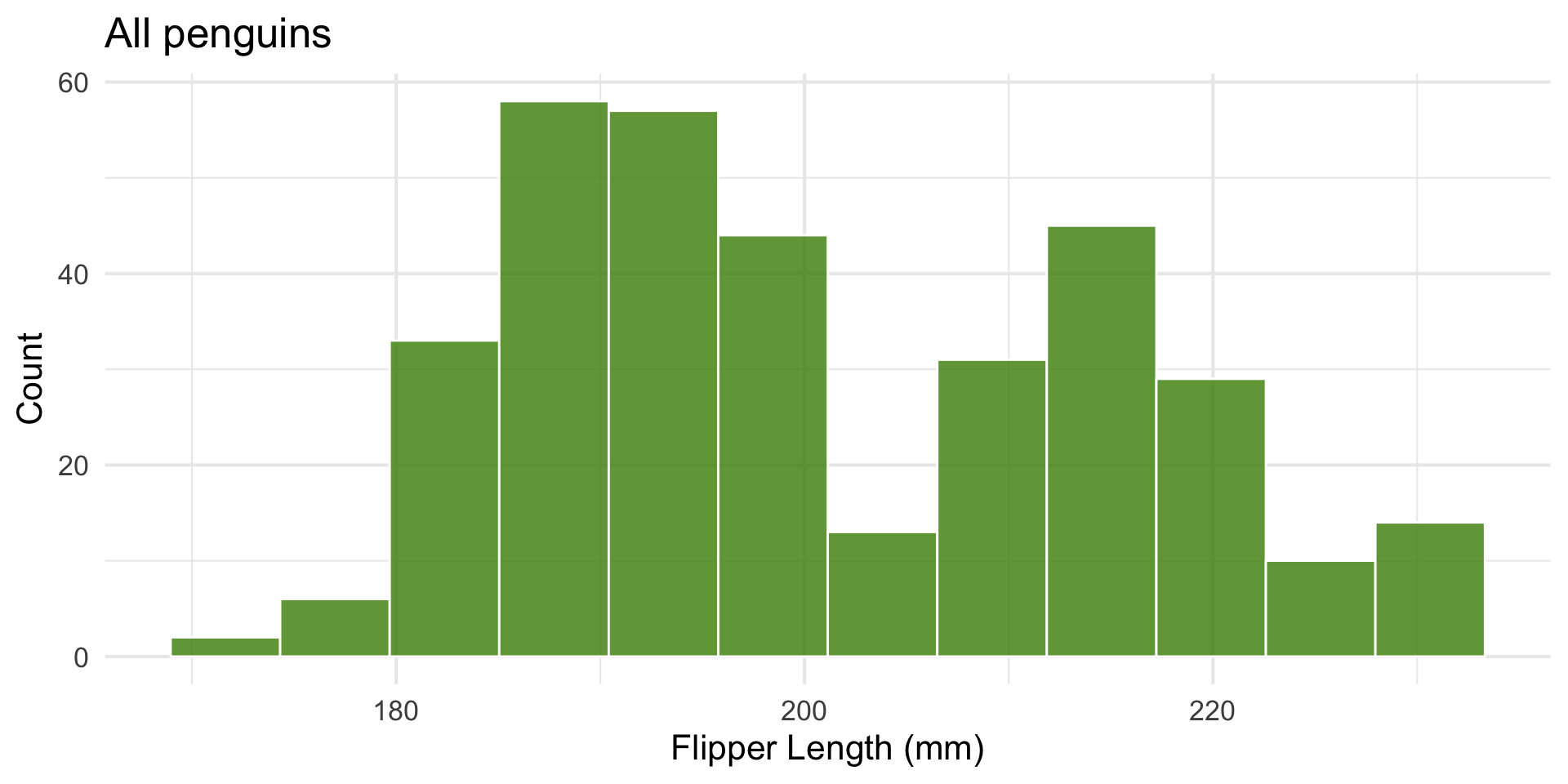
Look at one group’s distribution
Let’s look at penguin flipper length.
Filter for only ‘Adelie’.
Code
library(tidyverse)
library(palmerpenguins)
set.seed(7)
Adelie_penguins <- penguins |> filter(species == "Adelie")
ggplot(Adelie_penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm)) +
geom_histogram(fill = "chartreuse4", color = "white", bins = 12, alpha = 0.8) +
labs(
title = "151 Adelie penguins",
x = "Flipper Length (mm)",
y = "Count") + theme_minimal(base_size = 16)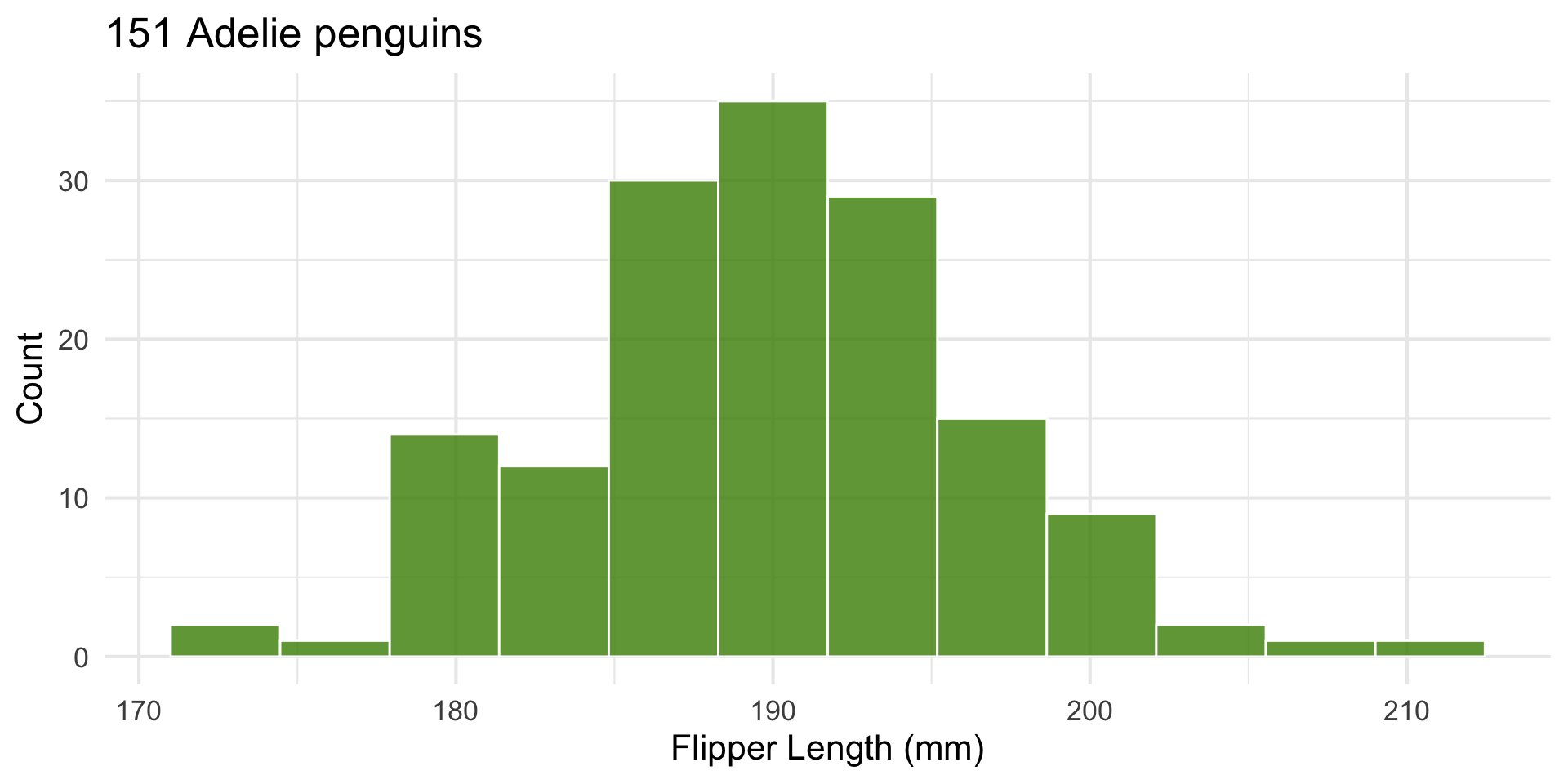
Undersampled vs. Well-sampled
Let’s look at penguin flipper length.
We’ll compare a tiny random sample to a large one.
Code
# Plot side by side
p_small <- ggplot(small_sample, aes(x = flipper_length_mm)) +
geom_histogram(fill = "chartreuse4", color = "white", bins = 8, alpha = 0.8) +
labs(
title = "Undersampled (n = 10)",
x = "Flipper Length (mm)",
y = "Count"
) +
theme_minimal(base_size = 16)
p_large <- ggplot(Adelie_penguins, aes(x = flipper_length_mm)) +
geom_histogram(fill = "chartreuse4", color = "white", bins = 12, alpha = 0.8) +
labs(
title = "151 Adelie penguins",
x = "Flipper Length (mm)",
y = "Count"
) +
theme_minimal(base_size = 16)
# Combine later with patchwork:
library(patchwork)
p_small + p_large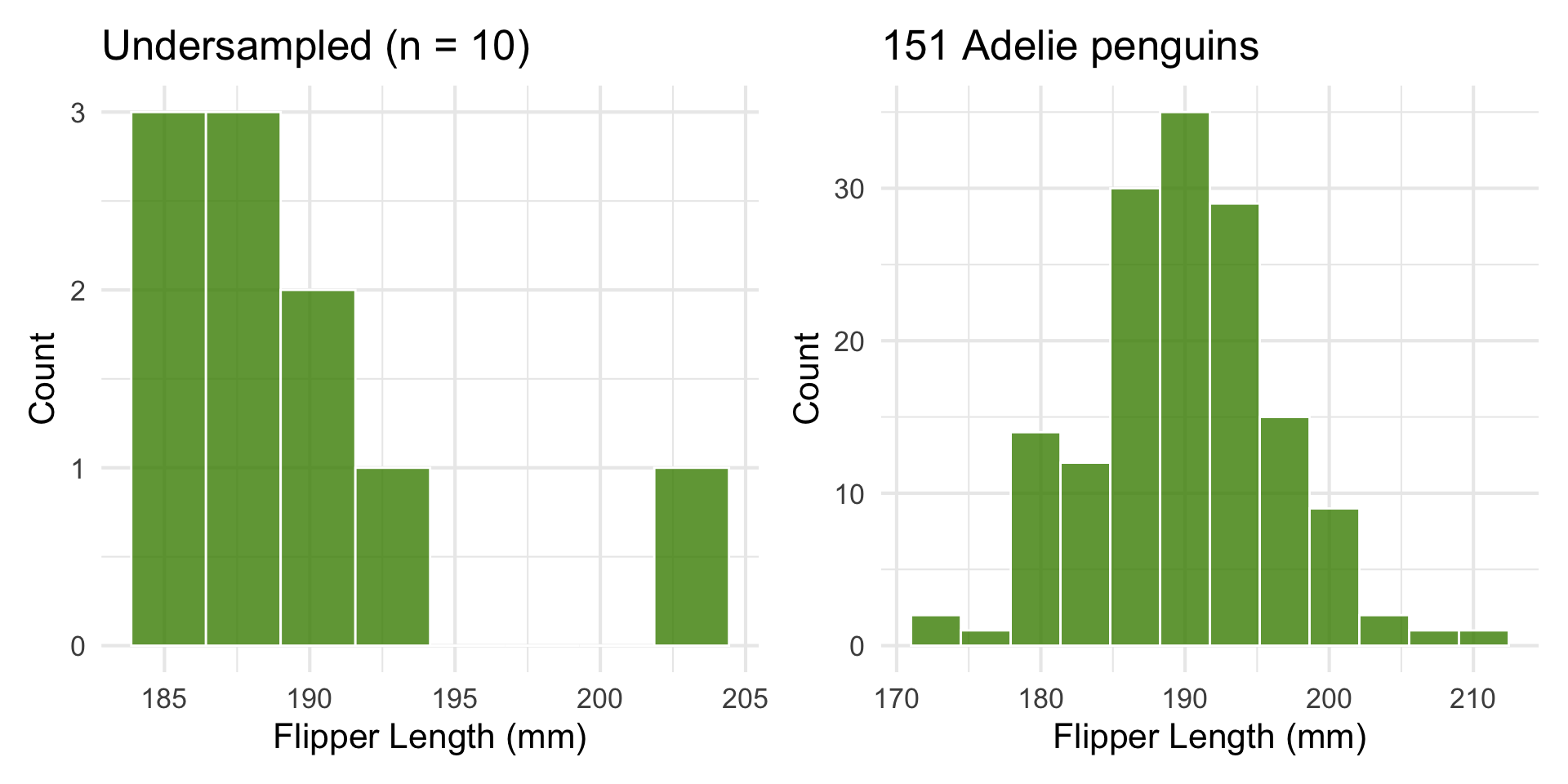
Why Measure Spread?
Two datasets can have the same center but very different variability.
We measure spread to understand how values differ from one another.
Common measures of spread so far:
- Range: max − min
- IQR (Interquartile Range): spread of the middle 50% of data
Range vs. IQR
| Measure | Description | Robust to Outliers? |
|---|---|---|
| Range | Distance from minimum to maximum | NO |
| IQR | Spread of the middle 50% of values | YES |
The IQR doesn’t change much even if the dataset has extreme values.
Example: IQR
We’ll use this data:
5, 9, 11, 14, 18, 21, 22
- Find the median (Q2)
- There are 7 observations (odd number).
- Median = 14
Example: IQR
Data: 5, 9, 11, 14, 18, 21, 22
Split the data. In the inclusive method, we include the median in both halves.
- Lower half is
5, 9, 11, 14
- Upper half is
14, 18, 21, 22
- Lower half is
Find Q1 and Q3
- Q1 = median of lower half = (9 + 11)/2 = 10
- Q3 = median of upper half = (18 + 21)/2 = 19.5
- Q1 = median of lower half = (9 + 11)/2 = 10
Compute the \(IQR = Q3 - Q1 = 19.5 - 10 = 9.5\)
Example: IQR
Why “inclusive” method?
We include the median in both halves so that each half represents half of the data up to and including the center.
This is the default method in R, Excel, and Google Sheets.
Summary
library(tidyverse)
data <- tibble(x = c(5, 9, 11, 14, 18, 21, 22))
# Summary of quartiles, IQR, range, etc.
data |>
summarize(
min_x = min(x),
q1_x = quantile(x, 0.25),
median = median(x),
q3_x = quantile(x, 0.75),
max_x = max(x),
iqr_x = IQR(x),
)# A tibble: 1 × 6
min_x q1_x median q3_x max_x iqr_x
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 5 10 14 19.5 22 9.5Boxplot
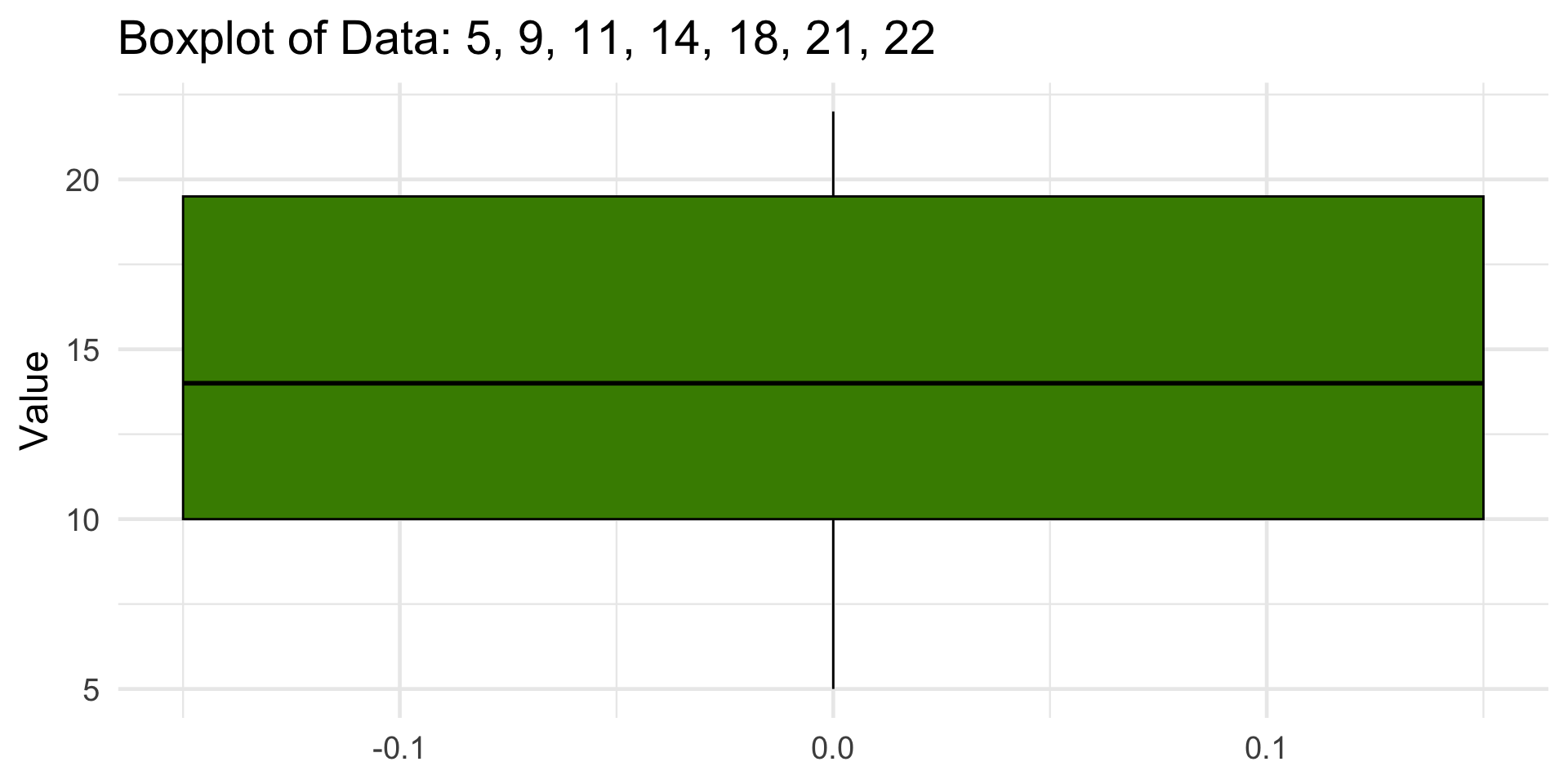
Example: Fences and Outliers
Let’s continue with the same data:
5, 9, 11, 14, 18, 21, 22
We already found that: Q1 = 10, Q3 = 19.5, IQR = 9.5
Compute the fences using the 1.5×IQR rule:
\[\text{Lower Fence} = Q1 - 1.5 \times IQR = 10 - 1.5(9.5) = -4.25\] \[\text{Upper Fence} = Q3 + 1.5 \times IQR = 19.5 + 1.5(9.5) = 33.75\]
- Any data values below -4.25 or above 33.75 would be considered outliers.
Check in R
library(tidyverse)
data <- tibble(x = c(5, 9, 11, 14, 18, 21, 22))
data |>
summarize(
min_x = min(x),
q1_x = quantile(x, 0.25),
median = median(x),
q3_x = quantile(x, 0.75),
max_x = max(x),
iqr_x = IQR(x),
lower_fence = q1_x - 1.5 * iqr_x,
upper_fence = q3_x + 1.5 * iqr_x
)# A tibble: 1 × 8
min_x q1_x median q3_x max_x iqr_x lower_fence upper_fence
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 5 10 14 19.5 22 9.5 -4.25 33.8Visualizing Outliers
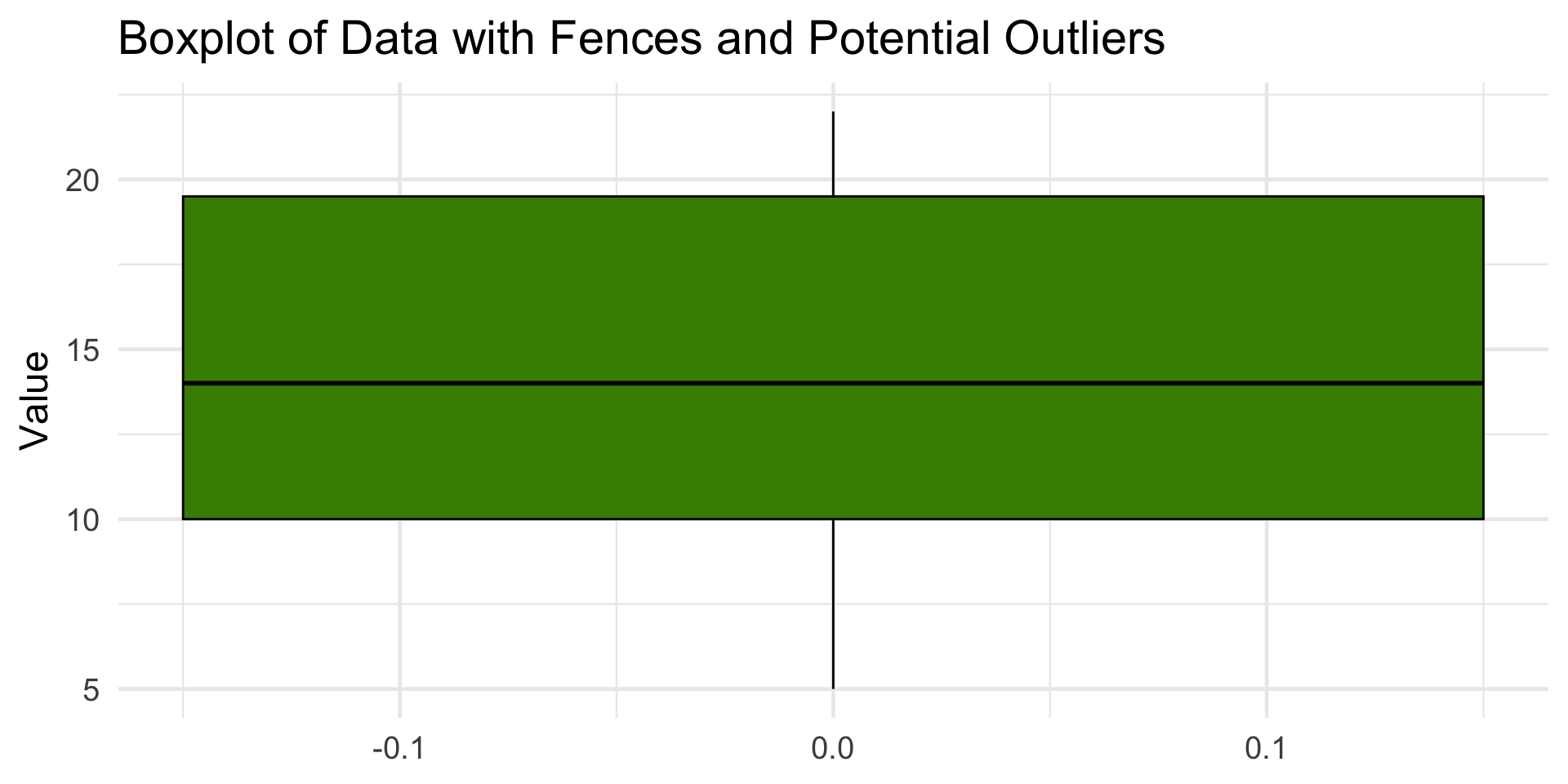
This dataset has no outliers, since all points fall between the fences (–4.25, 33.75).
Boxplots good for comparing distributions across categories
Try it out! Compute and Visualize by Hand
Dataset: 10, 2, 25, 8, 6, 12, 4
Pair up and compute the following by hand:
- Median
- Q1 and Q3
- Interquartile Range (IQR = Q3 − Q1)
- Lower and Upper Fences (1.5×IQR rule)
- Identify any potential outliers
Then sketch a rough boxplot of the data.
05:00
Check with R
data <- tibble(x = c(10, 2, 25, 8, 6, 12, 4))
data |>
summarize(
min_x = min(x),
q1_x = quantile(x, 0.25),
median = median(x),
q3_x = quantile(x, 0.75),
max_x = max(x),
iqr_x = IQR(x),
lower_fence = q1_x - 1.5 * iqr_x,
upper_fence = q3_x + 1.5 * iqr_x
)# A tibble: 1 × 8
min_x q1_x median q3_x max_x iqr_x lower_fence upper_fence
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2 5 8 11 25 6 -4 20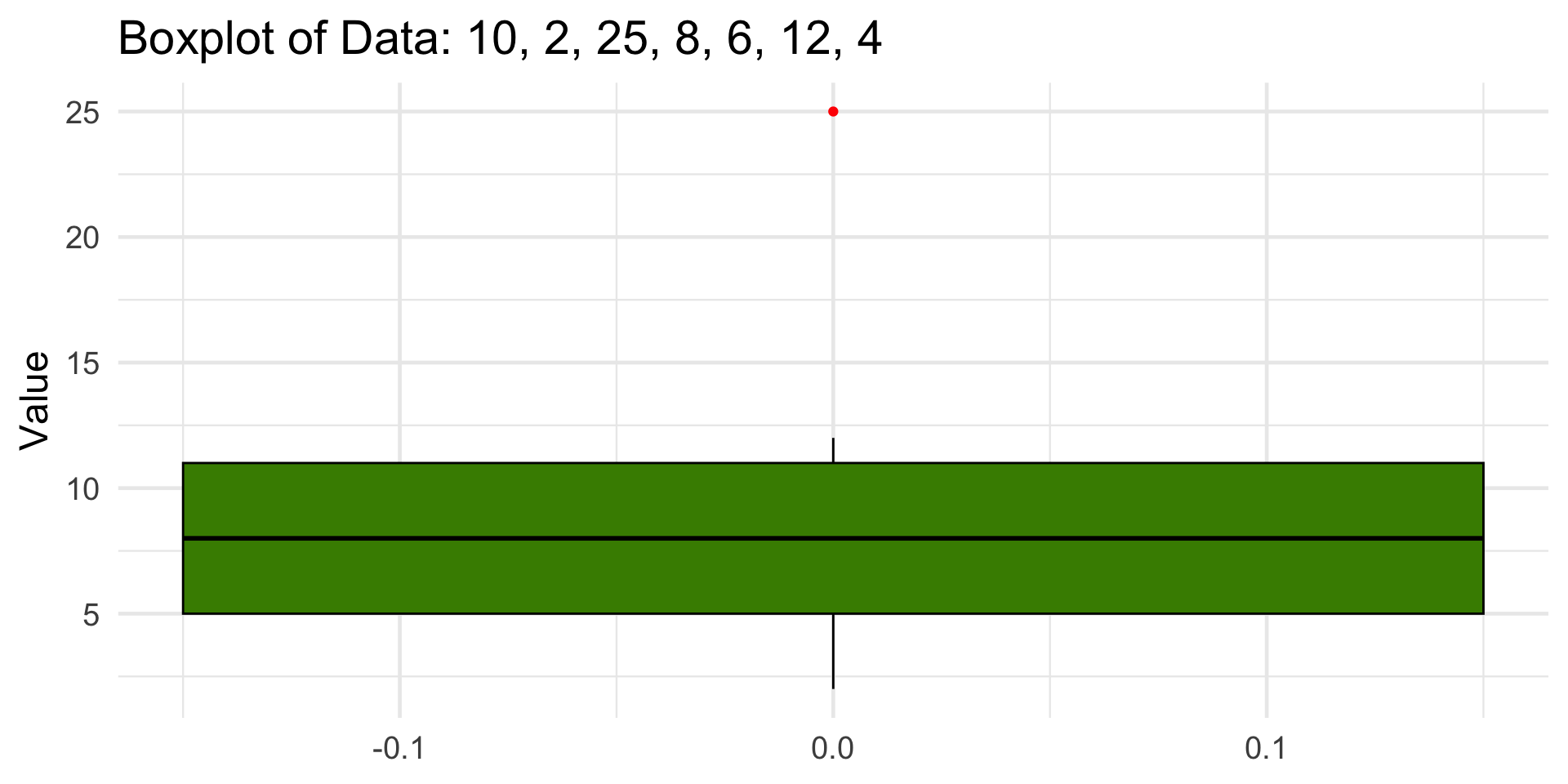
Variance and Standard Deviation
Variance and standard deviation measure how far values spread around the mean.
Variance
The variance (sample variance) is the average squared distance from the mean.
\[ \sigma^2 = \frac{\sum (x_i - \bar{x})^2}{n - 1} \]
Where:
- \(x_i\) — an individual data point
- \(\bar{x}\) — the sample mean (average of all data points)
- \(n\) — the number of observations in the sample
- \(\sigma^2\) — the sample variance (a measure of spread)
- \((x_i - \bar{x})\) — the deviation of each observation from the mean
Variance increases when data points are farther from the mean — it reflects how “spread out” the dataset is overall.
Standard Deviation
- The standard deviation (SD) is the square root of the variance.
- It’s in the same units as the data.
\[ \sigma = \sqrt{\sigma^2} \]
Standard Deviation
- A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean
- A high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range
Calculating Deviation from the Mean
- First, calculate the mean (\(\bar{x}\)) of the dataset.
- For each data point (\(x_i\)), calculate its deviation from the mean: \[x_i - \bar{x}\]
Square the Deviations
- Square each deviation to eliminate negative values: \[(x_i - \bar{x})^2\]
- Sum up all squared deviations: \[\sum_{i=1}^{n} (x_i - \bar{x})^2\]
- This sum represents the total squared deviation from the mean.
Calculating the Variance
- Divide the total squared deviation by \((n-1)\) (to account for the sample variance): \[\sigma^2 = \frac{1}{n-1} \sum_{i=1}^{n} (x_i - \bar{x})^2\]
- Using \((n-1)\) ensures an unbiased estimate of the population variance when calculating from a sample.
Deriving the Standard Deviation
- The standard deviation is the square root of the variance: \[\sigma = \sqrt{\sigma^2}\]
- Taking the square root converts the variance back to the units of the original data.
Example: Variance and SD by Hand
Data: 2, 4, 6, 8
- Mean = (2 + 4 + 6 + 8) / 4 = 5
- Compute each deviation:
\[ x_i - \bar{x} = \begin{cases} 2 - 5 = -3 \\ 4 - 5 = -1 \\ 6 - 5 = +1 \\ 8 - 5 = +3 \end{cases} \]
Example: Variance and SD by Hand
Data: 2, 4, 6, 8
Deviations: −3, −1, +1, +3
Square each deviation to remove negatives:
\[ (x_i - \bar{x})^2 = \begin{cases} (-3)^2 = 9 \\ (-1)^2 = 1 \\ (+1)^2 = 1 \\ (+3)^2 = 9 \end{cases} \]
Example: Variance and SD by Hand
Data: 2, 4, 6, 8
- Squared deviations: 9, 1, 1, 9
- Variance: \(\sigma^2 = \frac{9 + 1 + 1 + 9}{4 - 1} = \frac{20}{3} \approx 6.7\)
- Standard deviation: \(\sigma = \sqrt{6.7} \approx 2.6\)
Standard Deviation Calculation in R
Standard Deviation Calculation in R
Standard Deviation Calculation in R
Standard Deviation Calculation in R
Standard Deviation Calculation in R
Interpreting SD
- Small SD means data are tightly clustered around the mean
- Large SD means data are spread out
- Units: always the same as the data itself (e.g., cm, dollars, points)
Visual Comparison
Code
library(patchwork)
x <- tibble(x = rnorm(1000, mean = 0, 2))
a <- ggplot(x, aes(x = x )) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = .5, fill = "chartreuse4") + theme_bw(base_size = 14) +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean(x$x), color = "red", linewidth = 1) +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean(x$x) - sd(x$x), color = "blue", linetype = "dashed") +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean(x$x) + sd(x$x), color = "blue", linetype = "dashed") +
labs(
x = "Value",
y = "Count",
title = "A Distribution with Mean = 0, SD = 2"
) + xlim(-20, 20)
x <- tibble(x = rnorm(1000,mean = 0, 10))
b <- ggplot(x, aes(x = x )) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = .5, fill = "chartreuse4") + theme_bw(base_size = 14) +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean(x$x), color = "red", linewidth = 1) +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean(x$x) - sd(x$x), color = "blue", linetype = "dashed") +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean(x$x) + sd(x$x), color = "blue", linetype = "dashed") +
labs(
x = "Value",
y = "Count",
title = "A Distribution with Mean = 0, SD = 10"
) + xlim(-20, 20)
a + b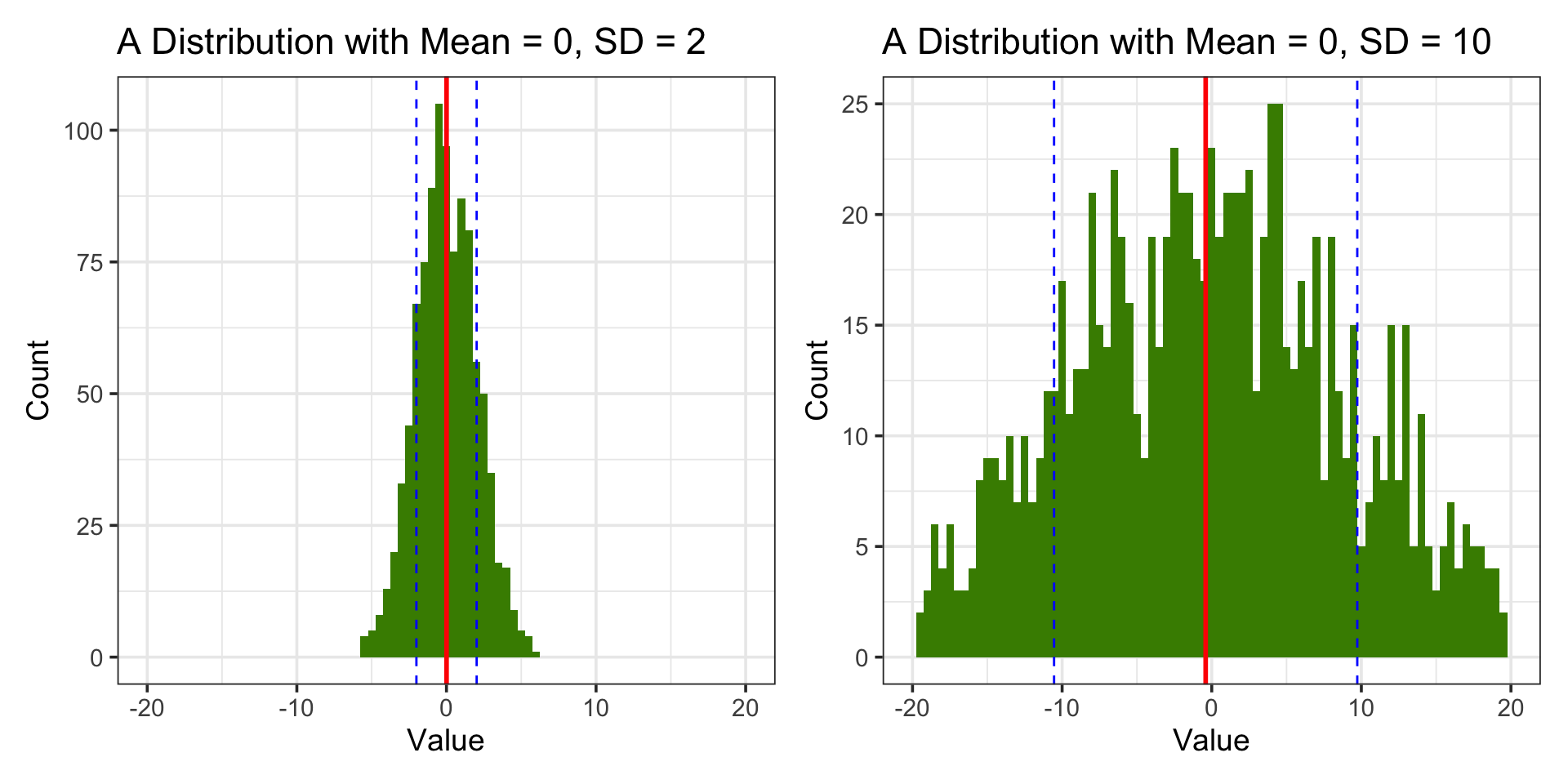
Summary
| Measure | What it Describes | Units | Robust to Outliers? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Entire spread | Same as data | NO |
| IQR | Middle 50% of data | Same as data | YES |
| Variance | Average squared distance | Squared units | NO |
| Standard Deviation | Typical distance from mean | Same as data | NO |
Z-Scores
A z-score tells how many standard deviations a value \(x\) is from the mean.
\[ z = \frac{x - \bar{x}}{\sigma} \]
- Positive is above the mean
- Negative is below the mean
- Values with \(|z| > 2\) are often considered unusual
Example: Calculating Z-Scores
Dataset: 2, 4, 6, 8
Mean = 5, SD ≈ 2.6
| x | z-score | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | (2−5)/2.6 ≈ −1.15 | below average |
| 4 | (4−5)/2.6 ≈ −0.38 | slightly below |
| 6 | (6−5)/2.6 ≈ +0.38 | slightly above |
| 8 | (8−5)/2.6 ≈ +1.15 | above average |
Compute in R
Interpreting Z-Scores
- A z-score of 0 means the value equals the mean.
- A z-score of +1 means 1 SD above the mean.
- A z-score of −1 means 1 SD below the mean.
- Extreme z-scores (e.g., beyond ±2 or ±3) may indicate outliers or rare events.
Visual Example
Code
library(ggplot2)
set.seed(7)
data <- tibble(x = rnorm(500, mean = 0, sd = 4))
mean_x <- mean(data$x)
sd_x <- sd(data$x)
ggplot(data, aes(x)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 30, fill = "chartreuse4", color = "white", alpha = 0.8) +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean_x, color = "red", linewidth = 1) +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean_x + c(-1, 1) * sd_x, color = "blue", linetype = "dashed") +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean_x + c(-2, 2) * sd_x, color = "purple", linetype = "dotted") +
labs(
title = "Standard Normal Distribution with Z-Scores",
x = "Value",
y = "Count"
) +
theme_minimal(base_size = 18) + annotate("text", x = mean_x -1.3, y = 40, label = "Mean (z = 0)", color = "red", vjust = -0.5) +
annotate("text", x = mean_x + sd_x -.7 , y = 40, label = "z = +1", color = "blue", vjust = -0.5) +
annotate("text", x = mean_x - sd_x -.7, y = 40, label = "z = -1", color = "blue", vjust = -0.5) +
annotate("text", x = mean_x + 2 * sd_x -.7, y = 40, label = "z = +2", color = "purple", vjust = -0.5) +
annotate("text", x = mean_x - 2 * sd_x - .7, y = 40, label = "z = -2", color = "purple", vjust = -0.5)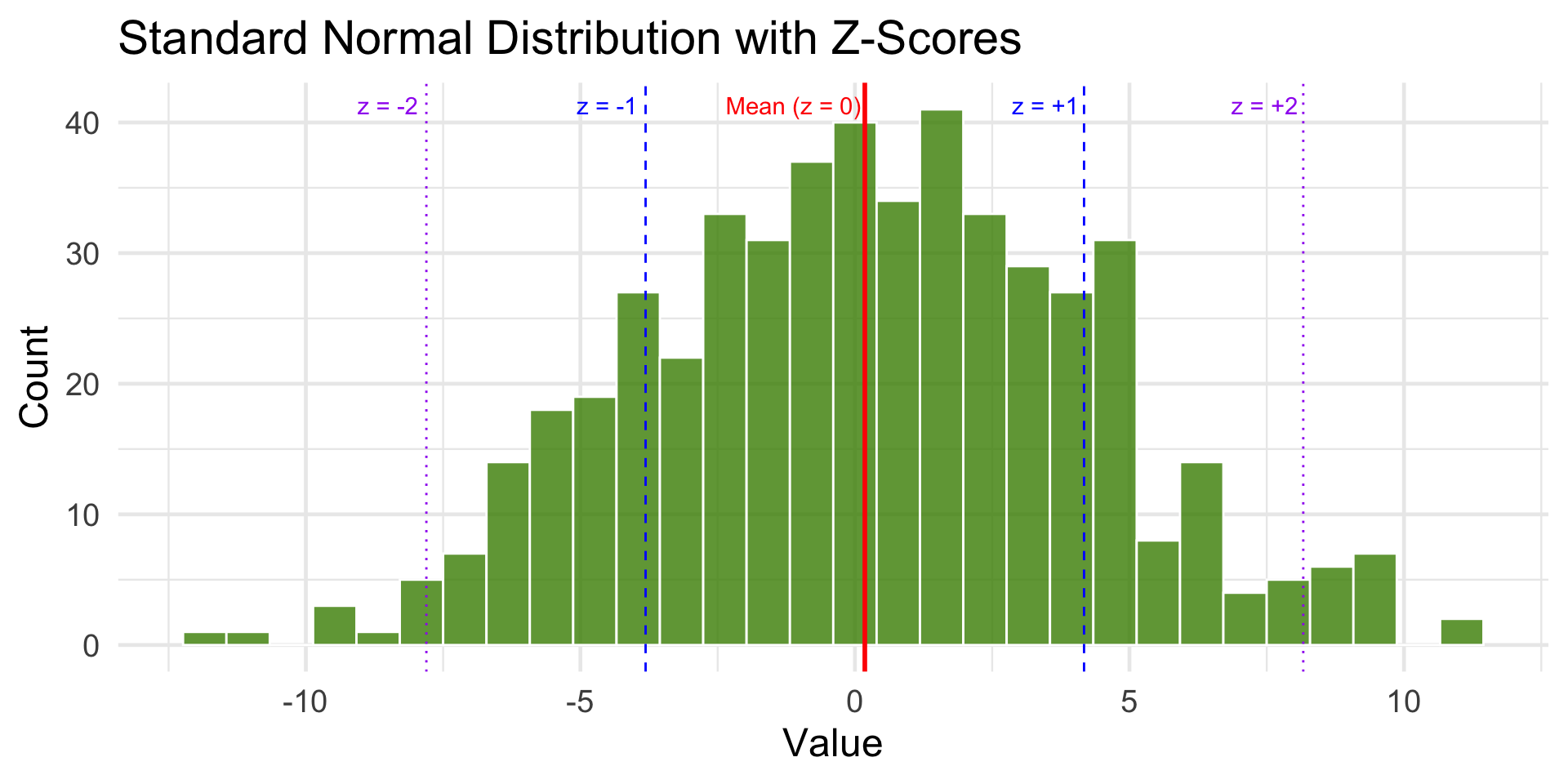
Visual Example: Z-score vs. IQR
Code
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
set.seed(7)
data <- tibble(x = rnorm(500, mean = 0, sd = 4))
# Mean and standard deviation (for z-scores)
mean_x <- mean(data$x)
sd_x <- sd(data$x)
# Median and IQR (for fences)
Q1 <- quantile(data$x, 0.25)
Q3 <- quantile(data$x, 0.75)
IQR_val <- IQR(data$x)
lower_fence <- Q1 - 1.5 * IQR_val
upper_fence <- Q3 + 1.5 * IQR_val
ggplot(data, aes(x)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 30, fill = "chartreuse4", color = "white", alpha = 0.8) +
# Mean and z-score lines
geom_vline(xintercept = mean_x, color = "red", linewidth = 1) +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean_x + c(-1, 1) * sd_x, color = "blue", linetype = "dashed") +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean_x + c(-2, 2) * sd_x, color = "purple", linetype = "dotted") +
# IQR and fence lines
geom_vline(xintercept = c(Q1, Q3), color = "orange", linetype = "solid", linewidth = 1) +
geom_vline(xintercept = c(lower_fence, upper_fence), color = "brown", linetype = "dashed") +
labs(
title = "Comparing Z-Scores and IQR Fences",
x = "Value",
y = "Count"
) +
theme_minimal(base_size = 18) +
# Z-score annotations
annotate("text", x = mean_x -1.3, y = 40, label = "Mean (z = 0)", color = "red", vjust = -0.5) +
annotate("text", x = mean_x + sd_x - .7 , y = 40, label = "z = +1", color = "blue", vjust = -0.5) +
annotate("text", x = mean_x - sd_x - .7, y = 40, label = "z = -1", color = "blue", vjust = -0.5) +
annotate("text", x = mean_x + 2 * sd_x - .7, y = 40, label = "z = +2", color = "purple", vjust = -0.5) +
annotate("text", x = mean_x - 2 * sd_x - .7, y = 40, label = "z = -2", color = "purple", vjust = -0.5) +
# IQR annotations
annotate("text", x = Q1, y = 45, label = "Q1", color = "orange", vjust = -0.5) +
annotate("text", x = Q3, y = 45, label = "Q3", color = "orange", vjust = -0.5) +
annotate("text", x = lower_fence, y = 30, label = "Lower Fence", color = "brown", angle = 90, vjust = -0.4) +
annotate("text", x = upper_fence, y = 30, label = "Upper Fence", color = "brown", angle = 90, vjust = -0.4)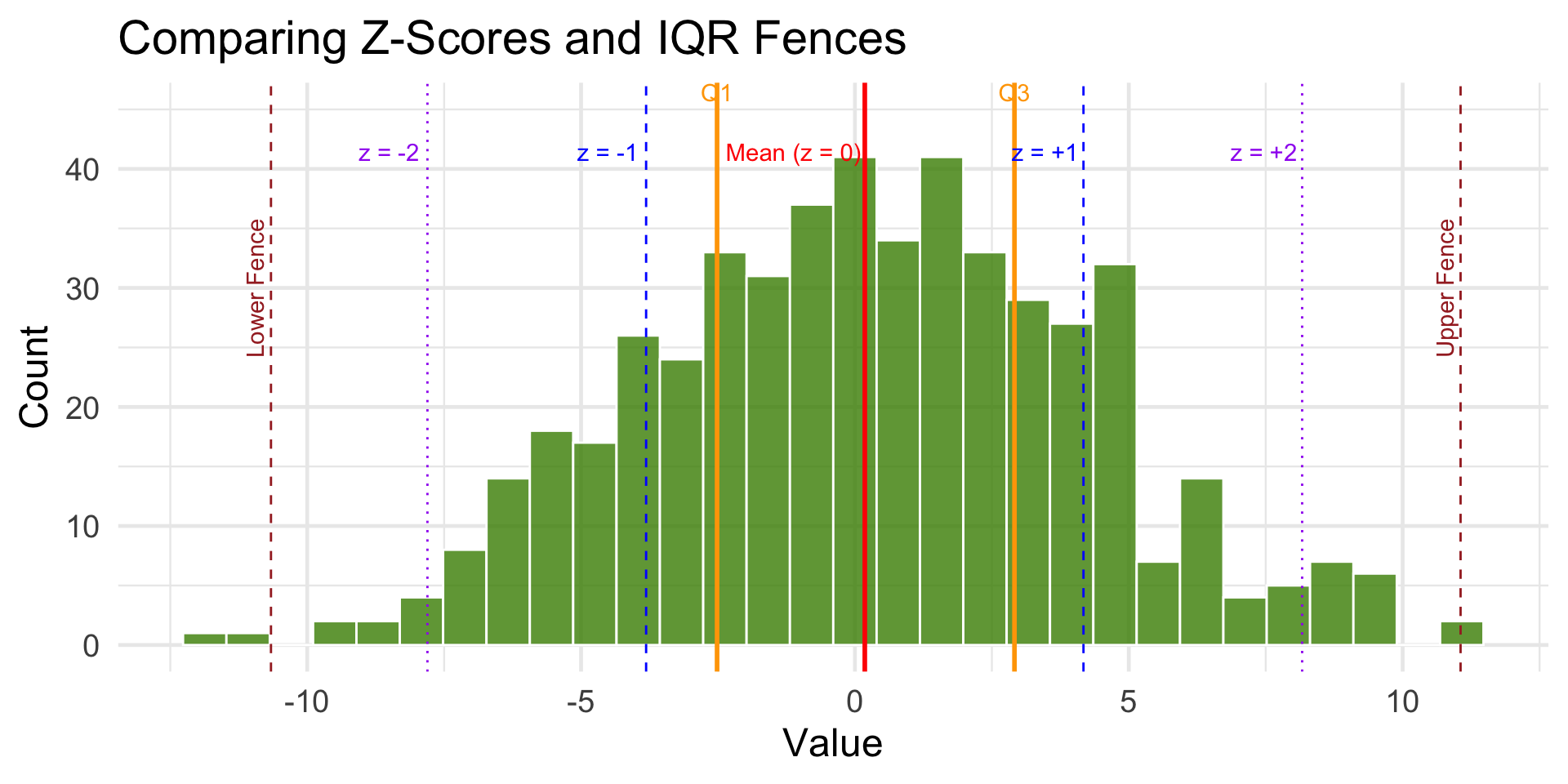
Summary of Outliers
| Type | Formula | Purpose | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Fence | Q1 - 1.5 × IQR Q3 + 1.5 × IQR |
Detects mild outliers | Standard boxplots |
| Extreme Fence | Q1 - 3 × IQR Q3 + 3 × IQR |
Detects extreme outliers | Detailed exploration |
| 2 SD Threshold | Mean ± 2 × SD | Captures ~95% of normal data | Quality control, z-scores |
| 3 SD Threshold | Mean ± 3 × SD | Flags rare deviations (~99.7%) | Detecting anomalies |